|
In 1939 the first public broadcast brought us a glimpse of the future of television. Barely 60 years later HDTV (High Definition Television), integrating computer functions, offers countless opportunities with hundreds of channels for our viewing entertainment.
The feasibility of performing chores and directing functions while we're away or creating an information superhighway library wherever one might be located is phenomenal.
TVs/Computers have taken center stage in residential plans and commercial settings, often becoming the focal point of a room with many rooms being created and designed specifically for a "theater" experience right in the home.
Below is a basic overview of the design criteria to consider when designing a home entertainment theater system.
HOME THEATER COMPONENTS:
1. VIDEO SOURCE: Cable, Laser Disc, Satellite, HiFi VCR, DVD
2. A/V RECEIVER: Dolby Pro Logic, Dolby Digital, THX, DTS, with "Surround Sound" capabilities (Hub to connect all equipment)
3. SPEAKERS: "Surround Sound," Wall-mounted or Floor-standing available.
4. SUBWOOFER: Highlights Low Frequencies (optional)
5. VIDEO DISPLAY: Direct "Tube," Front Projection, Rear Projection, HDTV, Flat Plasma
6. AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT: Universal remotes, tactile transducers/motion simulators
- THE PATH
> Line In > Decoder (DOLBY) > Audio Controls - Volume, Treble, etc. > Front Speakers: Left, Right and Center > USER < Back Speakers (Side Speakers if utilized)
- Test for comfort and ease of use.
- Determine the number of input and output jacks needed now and in the future
- All in one "Theater in a Box" combinations are great for small spaces, portability and the easiest to use, but they eliminate future upgrading possibilities |
UPGRADING A SYSTEM
- Individual components complying with Dolby standards for connectivity allow outdated technology and equipment to be upgraded easily
- Balancing the performance of different components is a principal consideration
- Quality speakers and additional speakers throughout a space will improve the A/V experience
- Gold plated inputs and outputs provide better connectivity
- Auto-sensing inputs help detect highest quality video signal
- Digital Signal Processing improves sound quality, simulates acoustics, ambiance and reverberation
- Speaker binding posts and banana plug connectors for the best possible connection
- Motion Simulators leading into virtual experiences
- Elaborate lighting effects and finishes
- Multi-room capabilities
- High-styling of cabinetry and components
ESTABLISHING SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
- Identify individual needs and uses of space (children, elderly, sports, gaming, etc.)
- Create a budget taking into consideration current equipment, current needs and future system requirements
- Specify new system requirements fitting your budget. NOTE: Select the best quality speakers' you can afford, as they determine the ultimate sound quality.
- Determine electrical distribution (basement up to the main floor or garage through the attic)
- Identify all elements for controlling temperature, utility consumption, appliances, security and A/V systems
- Establish control elements and connectivity accepting various protocols
- Plan for future needs and additional services that may be required
- Consider whether the system is user friendly (ergonomics), easy to install and operate, energy efficient, reliable and of the highest quality. Also consider service contracts and warranties provided by the manufacturer.
SPACE PLANNING REQUIREMENTS
- Establish whether the room will be used specifically for a theater or combined with other functions
- Detail a floor plan of the space under consideration
- Locate all main-bearing walls for wiring purposes
- Determine if access to adjacent rooms is required
- Establish optimum layout for seating, speakers, screen, equipment racks, etc.
- Place speakers in a symmetrical pattern. Adjustments of 6" or less will affect the overall results of the sound quality
- Avoid perfectly square rooms or rooms twice as long as they are wide
- Arrange furniture in a symmetrical pattern
- Center seating area between side-walls
- Identify sound reflecting surfaces, especially glass with no absorption properties
- Optimize acoustics for the best listening and viewing experience utilizing sound absorbing materials appropriate to the space
- Specify equipment relative to the room size
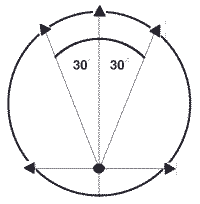
VIEWING DISTANCE CALCULATIONS
- A 60-degree arch (30 degrees to each side of a viewer) is considered optimal
- To establish the size of screen relative to the viewer, X = Y/1.8664 or Y=1.8664 X
X = horizontal (not diagonal) measurement of the screen
Y = distance from the screen to the viewer
If "Y" (the distance from the TV to the sitting area) equals 7' 0" ( 7 ÷ 1.8664 = X or 3.75 feet>
Conversely, if "X" (the width of the TV set) equals 3' 9" ( Y = 1.8664 x 3.75 or 7 feet )
- Use this calculation as a guide, not an absolute, to select the most comfortable viewing distance for you
VIDEO DISPLAY TYPES
1. DIRECT VIEW or "The Tube"
- Up to 40" diagonal
- Sharpest Picture
- Least Expensive Option
2. REAR PROJECTION or "Big Screen TV"
- Best suited for multi-functional rooms with natural light
- Red, Green and Blue lights
- Image projected on backside of screen
- Keep system sizes appropriate to room size and viewing distances
3. FRONT PROJECTION
- Red, Green and Blue lights
- Often projector is mounted to ceiling
- Image projected across the room onto a screen or light valued wall
- Room must be completely darkened with no natural lighting, if possible
- Electronic alignment for differing angels is available
- Auxiliary equipment can be added
- Screen can be retracted when not in use
4. HIGH DEFINITION TELEVISIONS (HDTV)
- Refers to systems with an internal ATSC tuner/decoder meeting widescreen specifications
- 16:9 Ratio
- Receives digital signals from broadcasters and cable companies offering six times the detail of normal analog broadcasts.
5. HIGH DEFINITION PERSONAL COMPUTERS (HDPC)
- Personal computer joined with a high definition TV, monitor and video projector (Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) or Digital Light Processing (DLP)
- Capable of delivering better picture with superior resolution (720 pixels or 720p)
- Software options
6. FLAT PLASMA SCREENS
- Work well in light and dark conditions
- Fits flat to the wall
- Large and easy to read with anti-glare filters
- 180 degree viewing angle prevents distortion from various viewing angles
- Can be hooked up to PC or MAC, VCR, DVD, Video Players, Video Conferencing, Security Monitors
- Great solution when Rear or Front Projection systems are not feasible.
SOUND QUALITY AND ACOUSTICS
- Consult a professional regarding acoustical treatments to improve the listening environment at little or no additional costs.
- Specify appropriate acoustical materials to absorb ceiling and side-wall reflections, as well as diffusing rear wall reflections to obtain the best results.
- Treat problem surfaces only for a "natural" live sound, rather than a sound with too many reflections, or a dead sound with no sound reflections.
- Install finishes prior to installation of audio/visual gear.
Creating a home theater is a popular home improvement and planning an elaborate system requires a specialist. But, you can spend time in a showroom to learn the differences between components or test a system. It is best to verify service agreements and warranties.
Avoid creating a difficult system to operate.
Everyone prefers a USER-FRIENDLY audio/visual experience that will "knock your socks off. "
- Dezignaré
|
